What is product development?
Product development — also called new product management — is a series of steps that includes the conceptualization, design, development and marketing of newly created or newly rebranded goods or services. Product development includes a product’s entire journey — from the initial idea to after its market release.
The objective of product development from a business standpoint is to cultivate, maintain and increase a company’s market share by satisfying consumer demand. From a customer standpoint, it’s to ensure value in the product as a quality good or service. Not every product will appeal to every customer or client base, so defining the target market for a product is a critical step that must take place early in the product development process. Organizations should conduct quantitative market research at all phases of the design process, including before the product or service is conceived, while the product is being designed and after the product has been launched.
Some organizations have product development centers that make products. For example, Alphabet Inc., Google’s parent company, launched a product development center in Kenya, Nairobi — as Alphabet is positioning itself to serve a growing base of internet users.
Product development frameworks
Although product development is creative, it requires a systematic approach to guide the processes required to get new products to market. Organizations such as the Product Development and Management Association (PDMA) and the Product Development Institute (PDI) help organizations select the best development framework for a new product or service. This framework helps structure the actual product development.
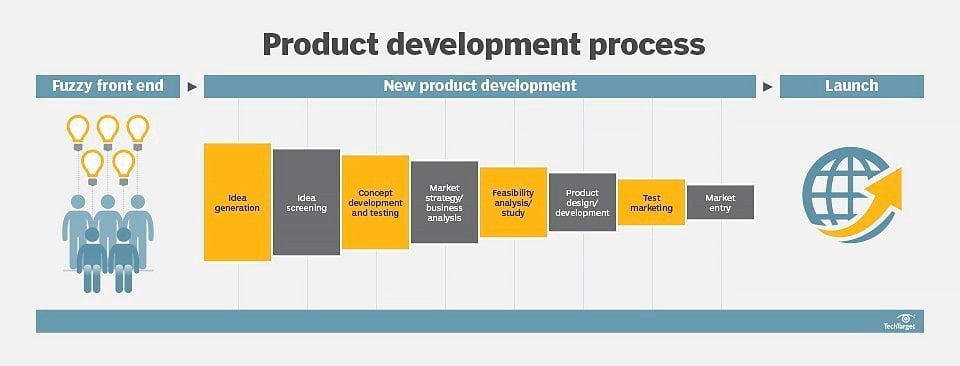
Some frameworks, such as the fuzzy front end (FFE) approach, define the steps that should be followed early in the development process, but leave it up to the product development team to decide in which order the steps make the most sense for the specific product that’s being developed. The five elements of FFE product development are as follows:
- Identification of design criteria entails brainstorming possible new products. Once an idea has been identified as a prospective product, a more formal product development strategy can be applied.
- Idea analysis requires a closer evaluation of the product concept. Market research and concept studies are conducted to determine if the idea is feasible or within a relevant business context to the company or to the consumer.
- Concept genesis involves turning an identified product opportunity into a tangible concept.
- Prototyping includes creating a rapid prototype for a product concept that has been determined to have business relevance and value.
- Product development requires ensuring the concept is viable and has been determined to make business sense and have business value.